- The Science of Sunspots: Understanding the Phenomenon
- The Importance of Sunlight: Health Benefits of Vitamin D
- Solar Eclipses: What Causes Them and How to View Them Safely
- The Structure of the Sun: Layers and Composition
- Solar Flares: How They Affect Earth and Our Technology
- The Mythology of the Sun: Cultures and Beliefs Across the World
- The Future of Solar Energy: Prospects and Challenges
- The Sun and Climate Change: How Solar Radiation Affects the Earth’s Temperature
- Sunbathing: Risks and Benefits of Excessive Exposure to Sunlight
- The Beauty of Sunrises and Sunsets: Photography and Art Inspiration.
The Science of Sunspots: Understanding the Phenomenon
Sunspots are fascinating phenomena that have captured the interest of astronomers and laypeople alike for centuries. These dark, irregularly shaped patches on the sun’s surface are caused by changes in the sun’s magnetic field, and they have a significant impact on the sun’s overall activity and the space weather that affects our planet.
Understanding the science behind sunspots is critical for scientists to predict and mitigate the effects of solar activity on Earth. Sunspots have been observed for hundreds of years, but it wasn’t until the invention of the telescope that astronomers were able to study them in detail.
Sunspots appear darker than the surrounding areas because they are cooler, with temperatures ranging from 3,500 to 4,500 degrees Celsius. By comparison, the temperature of the sun’s surface is around 5,500 degrees Celsius. Sunspots are created when magnetic fields from the sun’s interior become twisted and distorted, resulting in a concentration of magnetic energy on the surface. This energy inhibits the flow of hot gases from the sun’s interior, causing the temperature to drop and resulting in the dark, cool spot.
The number of sunspots on the sun’s surface varies over an 11-year cycle, known as the solar cycle. During times of high activity, the sun produces more sunspots, which can lead to solar flares and coronal mass ejections that can have significant effects on Earth’s climate and technology. For example, a strong solar storm in 1859 caused widespread disruption to telegraph systems and other early technologies, highlighting the importance of understanding and predicting the effects of solar activity.
Studying sunspots is an ongoing area of research for astronomers and solar physicists. By observing sunspots and other solar activity, scientists can learn more about the sun’s interior and magnetic field, which could help predict solar storms and improve our understanding of the sun’s impact on our planet.
The Importance of Sunlight: Health Benefits of Vitamin D
Sunlight is an essential element for life on Earth, and exposure to sunlight is critical for the production of vitamin D in the human body. Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy bones, teeth, and muscles and has numerous other health benefits.
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is produced when the skin is exposed to sunlight. When the sun’s ultraviolet rays come into contact with the skin, a chemical reaction occurs, and vitamin D is synthesized. However, many people do not get enough sunlight exposure, which can lead to a deficiency in vitamin D.
Vitamin D is essential for calcium absorption, which is necessary for healthy bones and teeth. Vitamin D deficiency can cause conditions such as rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults, which weaken bones and cause them to become soft and brittle. In addition to its role in bone health, vitamin D also helps to regulate the immune system, reducing the risk of infectious diseases.
Vitamin D has also been linked to a reduced risk of several chronic diseases, including cancer, diabetes, and heart disease. A study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that people with higher levels of vitamin D had a lower risk of developing colorectal cancer. Other studies have shown that vitamin D may help regulate insulin levels and improve cardiovascular health.
While sunlight is an essential source of vitamin D, it’s important to protect the skin from the harmful effects of the sun’s ultraviolet rays. Overexposure to sunlight can cause sunburn, skin damage, and increase the risk of skin cancer. The American Academy of Dermatology recommends using sunscreen with a minimum SPF of 30, wearing protective clothing, and seeking shade during peak sunlight hours to reduce the risk of skin damage.
In conclusion, exposure to sunlight is critical for the production of vitamin D in the human body, which plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy bones, teeth, and muscles, and reducing the risk of several chronic diseases. While it’s essential to protect the skin from the harmful effects of the sun, moderate exposure to sunlight is necessary for optimal health.
Solar Eclipses: What Causes Them and How to View Them Safely
Solar eclipses are among the most breathtaking and awe-inspiring celestial events that occur on Earth. They happen when the Moon passes between the Sun and the Earth, blocking the Sun’s light and creating a stunning display of light and shadow. However, watching a solar eclipse can be dangerous without proper precautions.
Solar eclipses occur when the Moon’s orbit aligns with the Sun and the Earth. This alignment causes the Moon to cast a shadow on the Earth’s surface, which creates the eclipse. There are three types of solar eclipses: total, partial, and annular. Total solar eclipses occur when the Moon completely covers the Sun, while partial and annular eclipses occur when the Moon only partially covers the Sun.
It’s important to note that viewing a solar eclipse can be dangerous without proper precautions. Looking directly at the Sun can cause serious eye damage or even blindness. The only safe way to view a solar eclipse is through specially designed solar filters, such as eclipse glasses or handheld solar viewers. These filters block harmful ultraviolet and infrared radiation and allow safe viewing of the eclipse.
It’s essential to follow the proper safety guidelines when viewing a solar eclipse. You should never look directly at the Sun without proper eye protection, even during a partial eclipse. You should also avoid using homemade filters, sunglasses, or other non-approved devices, which do not provide adequate protection.
To view a solar eclipse safely, you can use eclipse glasses or handheld solar viewers, which are readily available for purchase. You can also view the eclipse indirectly by projecting an image of the Sun onto a piece of paper using a pinhole camera or other projection device.
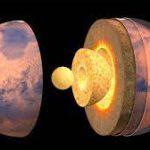
The Structure of the Sun: Layers and Composition
The Sun is the center of our solar system, and its structure is essential to understand how it functions and impacts our planet. The Sun is made up of several layers, each with unique characteristics and composition.
The innermost layer of the Sun is the core, where nuclear fusion takes place. The core is the hottest and densest part of the Sun, with temperatures reaching up to 15 million degrees Celsius. In the core, hydrogen atoms fuse to form helium, releasing energy in the process. This energy is the source of the Sun’s light and heat.
Surrounding the core is the radiative zone, which is about 200,000 kilometers thick. In the radiative zone, energy generated by nuclear fusion in the core is transported to the outer layers of the Sun through radiation. This process takes millions of years to complete.
The outermost layer of the Sun is the convective zone, which is about 200,000 kilometers thick. In this layer, energy is transported through the movement of hot plasma cells. The plasma cells rise from the bottom of the convective zone, carrying energy to the surface of the Sun, where it is released as heat and light.
Above the convective zone is the photosphere, the visible surface of the Sun. The photosphere has a temperature of about 5,500 degrees Celsius and emits most of the Sun’s visible light. The photosphere also contains sunspots, which are regions of cooler temperatures on the Sun’s surface.
Above the photosphere is the chromosphere, which is about 2,000 kilometers thick. The chromosphere emits a reddish-pink light and can only be seen during a solar eclipse.
The outermost layer of the Sun is the corona, a thin, hot atmosphere that extends millions of kilometers into space. The corona is visible during a total solar eclipse as a faint, white halo around the Sun.
The Sun is primarily made up of hydrogen and helium, which account for over 99% of its composition. Other elements, such as oxygen, carbon, and neon, make up the remaining 1%. The Sun’s composition is similar to that of other stars in the universe.
In conclusion, the Sun’s structure is comprised of several layers, each with unique characteristics and composition. Understanding the layers and composition of the Sun is essential to understanding its function and impact on our planet.
Solar Flares: How They Affect Earth and Our Technology
Solar flares are powerful bursts of energy that erupt from the Sun’s surface, releasing intense radiation and charged particles into space. While solar flares are fascinating astronomical events, they can also have a significant impact on Earth and our technology.
Solar flares occur when magnetic energy builds up in the Sun’s atmosphere and is suddenly released. These eruptions can last from a few minutes to several hours and can produce a range of effects, including intense bursts of X-rays and gamma rays, high-energy particles, and electromagnetic radiation.
The effects of solar flares on Earth can be both positive and negative. On the positive side, solar flares can produce beautiful auroras, also known as the Northern and Southern Lights. These stunning displays of colorful lights occur when charged particles from the Sun’s flares interact with Earth’s magnetic field.
On the negative side, solar flares can also have a significant impact on our technology. The charged particles released during a solar flare can interfere with radio communications, GPS systems, and satellite operations. This interference can cause significant disruptions in communication and navigation systems, which can have far-reaching consequences.
Solar flares can also cause power grid disruptions, which can lead to power outages and significant economic losses. In 1859, a massive solar flare known as the Carrington Event caused widespread telegraph disruptions and sparked auroras that were visible as far south as the Caribbean. If a similar event were to occur today, the impact on our technology and infrastructure could be catastrophic.
To mitigate the impact of solar flares on our technology, scientists and engineers are working on developing better warning systems and protective measures. For example, space weather satellites can provide early warning of incoming solar flares, giving us time to prepare and protect our technology.
In conclusion, solar flares are powerful astronomical events that can have both positive and negative effects on Earth and our technology. While solar flares can produce beautiful auroras, they can also cause significant disruptions in communication and navigation systems, as well as power grid disruptions. As our reliance on technology continues to grow, it’s essential to understand the impact of solar flares and develop better warning systems and protective measures to mitigate their impact.
The Mythology of the Sun: Cultures and Beliefs Across the World
The Sun has been a central part of human culture and belief systems since ancient times. Across the world, different cultures have developed unique mythologies and beliefs about the Sun, reflecting the importance of this celestial body in our lives.
In ancient Egypt, the Sun was worshipped as the god Ra, who was believed to travel across the sky in a boat. Ra was seen as a powerful and benevolent god, who brought warmth and light to the world.
In Greek mythology, the Sun was personified as Helios, who drove a chariot across the sky. Helios was believed to be a powerful and wise god, who could see everything happening on Earth.
In Hindu mythology, the Sun was worshipped as the god Surya, who was believed to bring light and warmth to the world. Surya was seen as a powerful and benevolent god, who could bring prosperity and good fortune to those who worshipped him.
In Native American mythology, the Sun was often seen as a powerful and benevolent spirit, who brought light and warmth to the world. Different tribes had different beliefs about the Sun, but it was generally seen as a symbol of life and renewal.
In many cultures, the Sun was also associated with creation and rebirth. The ancient Aztecs believed that the Sun was created by the god Quetzalcoatl, who sacrificed himself to create the world. In Norse mythology, the Sun was associated with the goddess Sunna, who drove a chariot across the sky and brought light and warmth to the world.
The Future of Solar Energy: Prospects and Challenges
Solar energy has become an increasingly popular source of renewable energy in recent years, with many countries investing in solar technology and infrastructure. However, as with any emerging technology, there are still challenges that need to be overcome before solar energy can reach its full potential.
One of the most significant challenges facing the widespread adoption of solar energy is cost. While the cost of solar panels has decreased significantly over the years, it still remains a significant investment for many households and businesses. Additionally, the cost of storage and distribution of solar energy can also be a barrier to its widespread adoption.
Another challenge facing solar energy is its intermittency. Unlike fossil fuels, solar energy is dependent on the availability of sunlight, which can vary depending on the time of day, season, and weather conditions. To overcome this challenge, researchers and engineers are working on developing better energy storage systems and smart grids that can manage the distribution of solar energy more effectively.
Despite these challenges, the prospects for solar energy are promising. Solar energy is a renewable and abundant source of energy, with the potential to provide clean energy to billions of people around the world. In many parts of the world, solar energy is already competitive with fossil fuels, and its cost is continuing to decrease.
Furthermore, the growth of solar energy has the potential to create significant economic opportunities, including the creation of new jobs and industries. As solar energy becomes more widespread, there will be an increasing demand for skilled workers in fields such as engineering, installation, and maintenance.
In conclusion, the future of solar energy is both promising and challenging. While cost and intermittency remain significant obstacles to its widespread adoption, the prospects for solar energy are bright. As technology and infrastructure continue to improve, solar energy has the potential to provide clean and abundant energy to people around the world, while creating new economic opportunities and reducing our dependence on fossil fuels.
The Sun and Climate Change: How Solar Radiation Affects the Earth’s Temperature
The Earth’s temperature is determined by a delicate balance of energy entering and leaving our planet. This balance is influenced by a variety of factors, including the Sun’s radiation. While the Earth’s temperature is primarily affected by greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, solar radiation can also play a role in shaping our climate.
Solar radiation is the energy emitted by the Sun and received by the Earth. The amount of solar radiation that reaches the Earth varies over time, due to factors such as the Sun’s activity and changes in the Earth’s orbit. When solar radiation enters the Earth’s atmosphere, it is either absorbed or reflected by the Earth’s surface, clouds, and atmosphere.
When more solar radiation is absorbed by the Earth than is reflected back into space, the Earth’s temperature increases. This can occur naturally due to changes in the Earth’s orbit, but it can also be influenced by human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels, which releases greenhouse gases that trap more heat in the Earth’s atmosphere.
While solar radiation can play a role in shaping the Earth’s climate, its influence is relatively small compared to greenhouse gases. Studies have shown that the variations in solar radiation over the past century have had only a small impact on the Earth’s temperature, and cannot account for the significant warming trend that has occurred in recent decades.
However, understanding the role of solar radiation in climate change is still important for predicting future climate patterns. As the Earth’s climate continues to change, it is possible that solar radiation could play a larger role in shaping our climate than it has in the past. Researchers are working to improve our understanding of the complex interactions between solar radiation and the Earth’s climate, in order to make more accurate predictions about future climate patterns.
In conclusion, while greenhouse gases are the primary driver of climate change, solar radiation can also play a role in shaping the Earth’s temperature. Understanding the influence of solar radiation on the Earth’s climate is important for predicting future climate patterns and developing strategies for mitigating the impacts of climate change. As our understanding of the Earth’s climate continues to evolve, it is crucial that we continue to study the complex interactions between solar radiation and the Earth’s atmosphere.
Sunbathing: Risks and Benefits of Excessive Exposure to Sunlight
Sunbathing, or the act of exposing one’s skin to the sun’s rays, has been a popular pastime for centuries. While some sun exposure is necessary for the body to produce vitamin D, excessive exposure to sunlight can have serious health consequences.
The primary risk of excessive sun exposure is skin damage, including sunburn, premature aging, and an increased risk of skin cancer. Sunburn occurs when the skin is exposed to more ultraviolet (UV) radiation than it can handle, causing redness, pain, and peeling. Repeated sunburns can increase the risk of skin cancer, including melanoma, which is the most deadly form of skin cancer.
In addition to skin damage, excessive sun exposure can also cause eye damage, including cataracts and macular degeneration. UV radiation can also weaken the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to fight off infections and diseases.
Despite these risks, there are also benefits to moderate sun exposure. Sunlight is necessary for the body to produce vitamin D, which is essential for strong bones and teeth. Additionally, exposure to sunlight can improve mood and mental health, as it stimulates the production of serotonin, a hormone that regulates mood.
To enjoy the benefits of sun exposure while minimizing the risks, it is important to take precautions when spending time in the sun. This includes wearing protective clothing, such as hats and long-sleeved shirts, and using sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. It is also important to avoid spending too much time in the sun during peak UV hours, which are typically between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
The Beauty of Sunrises and Sunsets: Photography and Art Inspiration
Sunrises and sunsets have long been a source of inspiration for artists and photographers alike. These moments, when the sun appears on the horizon or disappears below it, are some of the most beautiful and awe-inspiring natural phenomena. They provide a unique opportunity for capturing stunning images and creating beautiful works of art.
One of the most striking features of sunrises and sunsets is the range of colors they produce. The sky can turn a multitude of shades, from pinks and purples to oranges and yellows. These colors are created by the scattering of light as it passes through the Earth’s atmosphere. As the sun rises or sets, the light must travel through more of the atmosphere, causing the shorter wavelengths (blue and green) to scatter more, leaving behind the longer wavelengths (red and orange).
To capture the beauty of a sunrise or sunset, photographers must take into account the changing light and colors. The best times to photograph these moments are during the “golden hour,” which occurs just after sunrise or just before sunset. During this time, the light is softer and warmer, casting long shadows and creating a warm glow.
In addition to photography, sunrises and sunsets have also been a popular subject for artists throughout history. Famous painters such as Claude Monet and J.M.W. Turner were known for their stunning depictions of these moments, capturing the beauty and serenity of the changing light and colors.
The beauty of sunrises and sunsets can also inspire creativity in other areas, such as writing and poetry. The changing colors and light can evoke feelings of peace, tranquility, and hope, providing a rich source of inspiration for writers and poets.
In conclusion, the beauty of sunrises and sunsets is undeniable, providing endless inspiration for artists and photographers alike. By capturing the changing light and colors, these moments can create stunning images and works of art that evoke feelings of peace and tranquility. Whether through photography, painting, or writing, the beauty of sunrises and sunsets is a source of inspiration that has captivated us for centuries.
ScitechVenture YouTube Channel