- How Satellites Changed the World: A Brief History of Satellite Technology
- The Different Types of Satellites and Their Functions
- How Satellites are Launched into Space: The Science Behind It
- How Satellites Help in Weather Forecasting and Climate Change Studies
- The Role of Satellites in Global Navigation and GPS Technology
- How Satellites are Used in Telecommunications and Broadcasting
- Advancements in Satellite Imaging and Mapping Technologies
- The Importance of Satellites in Disaster Management and Emergency Response
- The Future of Satellite Technology: Trends and Innovations
- Environmental Impacts of Satellite Technology: Balancing the Benefits and Risks.
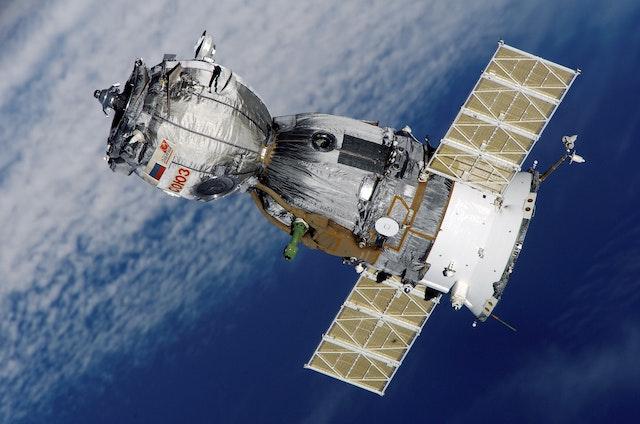
How Satellites Changed the World: A Brief History of Satellite Technology
Satellite technology has been a game-changer in many aspects of our lives, from communication to navigation to climate change research. The history of satellites is a fascinating one, marked by innovation, determination, and scientific breakthroughs.
In the 1950s, the Space Race between the United States and the Soviet Union was in full swing. The launch of the Soviet Union’s Sputnik 1 in 1957 marked the first successful launch of an artificial satellite. The United States responded with Explorer 1 in 1958, which discovered the Van Allen radiation belts surrounding Earth. These early satellites laid the groundwork for future developments in satellite technology.
As satellite technology advanced, so did its uses. Satellites became crucial for military intelligence gathering during the Cold War. In the 1960s and 1970s, weather satellites were developed to monitor weather patterns and provide early warning of severe weather events. Navigation satellites like GPS have revolutionized the way we travel, making it possible to navigate even the most remote areas of the world with pinpoint accuracy.
The launch of communication satellites in the 1960s changed the face of global communication. Satellites made it possible to transmit information across vast distances, connecting people and businesses like never before. Today, we rely on satellites for everything from television broadcasting to mobile phone service.
The development of remote sensing satellites in the 1970s allowed scientists to study our planet from space. Satellites equipped with sensors and cameras provide critical data on everything from crop yields to deforestation to climate change. These data have helped us better understand our planet and make informed decisions about its future.
The Different Types of Satellites and Their Functions
Satellites are an essential part of modern life. These machines are used in a variety of ways, from communication and navigation to scientific research and national security. There are several types of satellites, each with its own unique set of functions and capabilities.
One of the most common types of satellites is the communication satellite. These satellites are used to transmit information between two or more points on Earth. They are responsible for our ability to make phone calls, send text messages, and access the internet from almost anywhere on the planet.
Another type of satellite is the navigation satellite, which is used for GPS and other location-based services. Navigation satellites use a network of satellites in space to provide accurate positioning data to users on Earth. This technology is used in everything from smartphones to airplanes.
Remote sensing satellites are another type of satellite that are used in scientific research. These satellites are equipped with sensors and cameras that can capture detailed images and data about the Earth’s surface. Scientists use this data to study everything from weather patterns to crop yields to climate change.
Military and intelligence agencies also use satellites for reconnaissance and surveillance purposes. These satellites are equipped with advanced sensors that can detect enemy movements, monitor nuclear activity, and gather other critical intelligence.
There are also several other types of satellites, including weather satellites, scientific research satellites, and space telescopes. Each of these types of satellites has a unique set of functions and capabilities, and they all play a critical role in our modern world.
How Satellites are Launched into Space: The Science Behind It
Satellites are launched into space using a variety of different methods, each with its own unique set of challenges and requirements. The science behind launching satellites into space is complex and requires a deep understanding of physics, engineering, and rocket science.
One of the most common methods for launching satellites into space is through the use of rockets. Rockets are powerful vehicles that can generate enough thrust to overcome the Earth’s gravity and propel satellites into orbit. These rockets can be launched from a variety of different locations, including launch pads on the ground, aircraft, and even from ships at sea.
The process of launching a satellite into space begins long before the rocket is even built. Engineers and scientists must carefully design the satellite and the rocket to ensure that they are compatible and can function properly in the harsh conditions of space. This includes considerations such as the weight and size of the satellite, the type of fuel used in the rocket, and the trajectory of the launch.
Once the satellite and rocket have been designed and built, they are transported to the launch site and prepared for launch. This process can take several weeks or even months, as technicians and engineers perform a variety of tests and checks to ensure that everything is working properly.
When the rocket is finally launched, it undergoes several stages of acceleration and separation as it moves towards orbit. At each stage, different components of the rocket are jettisoned, allowing the remaining parts to continue their ascent into space.
Once the rocket has reached the desired altitude, the satellite is released from the rocket and begins its mission in space. This may involve maneuvering into a specific orbit, deploying solar panels, and activating various scientific instruments.
How Satellites Help in Weather Forecasting and Climate Change Studies
Satellites play a crucial role in weather forecasting and climate change studies, providing scientists and meteorologists with valuable data and insights about our planet’s climate and weather patterns. Satellites are used to track everything from hurricanes and tornadoes to droughts and heatwaves, helping us to better understand and predict weather patterns and their effects on our planet.
One way that satellites help in weather forecasting is by providing real-time data about atmospheric conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure. This data is collected by sensors on the satellite and transmitted back to Earth, where it can be analyzed and used to create weather models and forecasts.
Satellites are also used to track severe weather events, such as hurricanes and tornadoes. By tracking the movement and intensity of these storms from space, scientists and meteorologists can better predict their path and potential impact, allowing communities to prepare and take necessary precautions.
In addition to weather forecasting, satellites are also used to study climate change and its effects on our planet. Satellites can track changes in sea level, temperature, and ice coverage, providing scientists with valuable data about the health of our planet’s ecosystems.
Satellites can also track changes in the Earth’s atmosphere, such as the levels of greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide. By tracking these changes over time, scientists can better understand the impact of human activity on the planet’s climate and develop strategies to mitigate its effects.
The Role of Satellites in Global Navigation and GPS Technology
Satellites play a crucial role in global navigation and GPS technology, allowing us to accurately determine our location and navigate to our destination. GPS, or Global Positioning System, is a network of satellites that orbit the Earth and transmit signals to GPS receivers on the ground. These signals are used to determine the receiver’s location and provide directions to a specific destination.
GPS technology has revolutionized the way we navigate and travel, providing accurate and reliable directions to drivers, hikers, and pilots around the world. This technology has also had a significant impact on logistics and transportation industries, enabling companies to track the location of their vehicles and goods in real-time.
The GPS system relies on a network of 24 satellites, which are constantly orbiting the Earth at an altitude of approximately 12,500 miles. These satellites are equipped with atomic clocks and are synchronized with each other, allowing them to accurately measure the distance between the satellite and the GPS receiver on the ground.
When a GPS receiver receives signals from multiple satellites, it can calculate its exact location by triangulating the distance between the satellites and the receiver. This information is then used to provide directions to the user, as well as information about their speed and direction of travel.
In addition to GPS technology, satellites are also used for other forms of global navigation, such as the GLONASS system operated by Russia and the BeiDou system operated by China. These systems use similar technology to GPS and provide their own set of benefits and applications.
How Satellites are Used in Telecommunications and Broadcasting
Satellites have had a profound impact on telecommunications and broadcasting, providing a means of transmitting information over long distances without the need for physical cables or infrastructure. Satellites orbiting the Earth are used to provide a range of telecommunications and broadcasting services, including television and radio broadcasting, mobile phone networks, and internet connectivity.
Satellites used for telecommunications and broadcasting are typically placed in geostationary orbit, which means they remain in a fixed position relative to the Earth’s surface. This allows them to provide continuous coverage to a specific region or area, without the need to constantly reposition the satellite.
Television and radio broadcasters use satellites to transmit their signals to a wider audience. These signals are sent from the broadcasting station to the satellite, which then beams them down to a receiver on the ground. This allows broadcasters to reach a global audience, without the need for physical infrastructure like cables and transmission towers.
Satellites are also used to provide mobile phone and internet connectivity in remote or hard-to-reach areas. This is done through the use of satellite phones and modems, which connect to the satellite and allow users to make calls or access the internet. This technology has been particularly useful in areas where traditional infrastructure like cell towers or fiber optic cables is not feasible or cost-effective.
In addition to telecommunications and broadcasting, satellites are also used for scientific research and exploration. For example, satellites like the Hubble Space Telescope have provided unprecedented insights into the universe, allowing scientists to study galaxies and other celestial bodies in unprecedented detail.
Advancements in Satellite Imaging and Mapping Technologies
Satellite imaging and mapping technologies have come a long way in recent years, providing us with detailed and accurate information about the Earth’s surface and its features. From mapping the world’s terrain to monitoring natural disasters, satellite imaging and mapping technologies have become an essential tool for a wide range of industries and applications.
One of the key advancements in satellite imaging and mapping technologies is the development of high-resolution imaging systems. These systems use advanced sensors and cameras to capture images of the Earth’s surface in unprecedented detail, allowing us to study and monitor changes to the landscape and environment over time.
Satellite imaging and mapping technologies are also used to study and monitor natural disasters like earthquakes, hurricanes, and wildfires. These technologies allow emergency responders to quickly assess the extent of the damage and plan their response accordingly, potentially saving lives and minimizing the impact of these events on communities and infrastructure.
Satellite imaging and mapping technologies have also become a critical tool for environmental monitoring and conservation efforts. These technologies can be used to study and monitor changes to ecosystems, track deforestation and land use changes, and even monitor the impact of climate change on the Earth’s surface.
In addition to their applications on Earth, satellite imaging and mapping technologies are also used for space exploration and research. Satellites like NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter use advanced imaging systems to study the surface of other planets, providing scientists with valuable information about the history and geology of these distant worlds.
Overall, the advancements in satellite imaging and mapping technologies have provided us with an unprecedented level of detail and accuracy about the Earth’s surface and its features. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in this field, potentially leading to new applications and insights into our planet and the universe beyond.
The Importance of Satellites in Disaster Management and Emergency Response
Satellites play a crucial role in disaster management and emergency response, providing critical information and support to first responders and relief efforts. In the event of a natural disaster or emergency situation, satellite technology can be used to quickly assess the damage and facilitate a coordinated response.
One of the key advantages of satellite technology in disaster management is its ability to provide real-time monitoring and imaging of affected areas. This allows responders to quickly assess the extent of the damage and prioritize their response efforts. For example, satellites can be used to detect changes in terrain or water levels, identify areas where people may be stranded, and locate critical infrastructure like hospitals and power stations.
Satellites can also be used to provide communication and navigation support in disaster situations. In areas where traditional communication infrastructure has been damaged or destroyed, satellite phones and modems can be used to establish communication links between responders and affected communities. Satellites can also be used to provide accurate GPS coordinates and mapping information, which is essential for search and rescue efforts.
In addition to their applications during disaster situations, satellites also play a critical role in preparedness and mitigation efforts. For example, satellites can be used to monitor weather patterns and predict the likelihood of natural disasters like hurricanes, tornadoes, and floods. This information can be used to alert communities and take preventative measures to minimize the impact of these events.
Overall, the importance of satellites in disaster management and emergency response cannot be overstated. From real-time imaging and monitoring to communication and navigation support, satellite technology provides critical information and tools that are essential for saving lives and minimizing the impact of natural disasters and emergency situations. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more innovative applications of satellite technology in disaster management and emergency response.
The Future of Satellite Technology: Trends and Innovations
Satellite technology has come a long way since the launch of the first artificial satellite, Sputnik, in 1957. Today, satellites are used for a wide range of applications, from communication and navigation to weather forecasting and environmental monitoring. As technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more exciting developments and innovations in the field of satellite technology.
One of the key trends in satellite technology is the miniaturization of satellites. Small satellites, also known as CubeSats, are becoming increasingly popular due to their lower costs and greater flexibility. These miniature satellites are often used for scientific research, environmental monitoring, and communication purposes, and can be launched in large numbers to provide broader coverage and more detailed information.
Another trend in satellite technology is the development of high-throughput satellites (HTS). These advanced satellites use multiple spot beams to provide high-speed data transfer rates, making them ideal for applications like high-speed internet and video streaming. HTS are also more efficient than traditional satellites, allowing for greater bandwidth and data transfer capabilities.
In addition to miniaturization and high-throughput technology, the use of artificial intelligence (AI) is also becoming increasingly important in satellite technology. AI can be used to analyze large amounts of data collected by satellites, allowing for more accurate and timely decision-making. AI can also be used to optimize the performance of satellites, predicting potential problems and adjusting operations to maximize efficiency.
Finally, the use of 3D printing technology is also becoming more prevalent in satellite design and production. This technology allows for faster and more cost-effective production of satellite components, and can also be used to create complex and customizable designs that were previously impossible to produce.
Environmental Impacts of Satellite Technology: Balancing the Benefits and Risks.
Satellite technology has revolutionized many industries and provided a wide range of benefits, from communication and navigation to weather forecasting and disaster management. However, like any technology, satellite systems also have environmental impacts that need to be carefully considered and managed.
One of the primary environmental impacts of satellite technology is the increase in space debris. As more satellites are launched into orbit, the risk of collisions and the resulting debris increases. This debris can pose a threat to other satellites, spacecraft, and even astronauts, and can remain in orbit for many years, further increasing the risk of collisions.
Another environmental impact of satellite technology is the energy required to launch and operate satellites. The production of rockets and the fuel used to launch them can have significant environmental impacts, including carbon emissions and the depletion of natural resources. Additionally, satellites require a constant supply of power to operate, which can come from non-renewable sources, such as fossil fuels.
Satellite technology can also have impacts on wildlife and ecosystems. For example, some birds use the Earth’s magnetic field for navigation, and satellite signals can disrupt this ability, potentially causing harm to bird populations. Satellite imaging can also be used to track and monitor wildlife, but this can be invasive and can have unintended consequences, such as disturbing the animals or disrupting their habitats.
Despite these environmental impacts, satellite technology also has the potential to support environmental sustainability efforts. For example, satellites can be used to monitor and track environmental changes, such as deforestation, land use changes, and ocean acidification. This information can be used to inform policy decisions and support conservation efforts. Additionally, satellite technology can support renewable energy development, such as solar and wind power, by providing real-time data on weather patterns and energy production.
Overall, the environmental impacts of satellite technology must be carefully considered and managed to ensure that the benefits of this technology are balanced against the risks. Steps can be taken to minimize these impacts, such as reducing space debris through responsible satellite disposal practices and using renewable energy sources to power satellites. By working to minimize the environmental impacts of satellite technology, we can ensure that this valuable technology continues to support a wide range of applications while also supporting sustainability efforts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, satellite technology has changed the world in numerous ways, from improving communication and navigation to supporting disaster management and climate change studies. However, as with any technology, satellite systems also have environmental impacts that must be carefully considered and managed. The increase in space debris, the energy required to launch and operate satellites, and impacts on wildlife and ecosystems are just a few examples of the environmental impacts of satellite technology. Despite these impacts, satellite technology also has the potential to support environmental sustainability efforts, such as monitoring and tracking environmental changes and supporting renewable energy development. By balancing the benefits and risks of satellite technology and working to minimize its environmental impacts, we can ensure that this valuable technology continues to support a wide range of applications while also supporting sustainability efforts.
ScitechVenture YouTube Channel