- The Moon: An Overview of Its Formation and Characteristics
- The Cultural Significance of the Moon Across Different Civilizations
- The Role of the Moon in Shaping Earth’s Tides and Climate
- The Moon Landing: A Historic Achievement and Its Legacy
- Lunar Phases: Understanding the Waxing and Waning of the Moon
- The Dark Side of the Moon: Myths and Realities
- Lunar Exploration: Past, Present, and Future Missions
- The Moon’s Effect on Wildlife and Ecosystems
- Moon Myths and Legends: Separating Fact from Fiction
- Lunar Observations: Tips and Tools for Stargazers and Astronomers
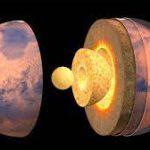
The Moon: An Overview of Its Formation and Characteristics
The Moon, a celestial body that has fascinated humans for centuries, is the Earth’s only natural satellite. Understanding its formation and characteristics can provide insight into the evolution of our solar system. In this blog, we will explore the formation and features of the Moon, using an active voice to bring the subject to life.
Scientists believe that the Moon formed about 4.5 billion years ago, shortly after the birth of the solar system. The most widely accepted theory is that a Mars-sized object collided with Earth, throwing debris into space, which eventually coalesced to form the Moon.
The Moon has a rocky surface that is heavily cratered, due to billions of years of bombardment by meteoroids. It has no atmosphere, and its surface temperature ranges from -173°C to 127°C. The Moon’s surface is also covered in a fine layer of dust, known as regolith, which was created by the constant impact of meteoroids.
The Moon’s size is approximately one-quarter that of Earth’s, and it orbits around our planet at an average distance of about 238,855 miles (384,400 kilometers). Its gravitational pull on Earth causes the ocean tides, and its rotation is synchronized with its orbit, meaning that the same side always faces Earth.
The Moon’s phases are caused by its position relative to the Sun and Earth. As the Moon orbits Earth, the amount of sunlight it reflects changes, creating the familiar waxing and waning phases. During a full moon, the entire surface facing Earth is illuminated by the Sun.
In recent years, there has been renewed interest in exploring the Moon. NASA plans to establish a permanent lunar base by the end of the decade, while private companies are also developing plans for lunar missions. Such exploration could provide valuable insights into the Moon’s history and help us to better understand the origins of our solar system.
The Cultural Significance of the Moon Across Different Civilizations
The Moon has played an important role in human culture and history, inspiring myths, legends, and religious beliefs across civilizations throughout the ages. In this blog, we will explore the cultural significance of the Moon across different civilizations, using an active voice to bring the subject to life.
In ancient Egypt, the Moon was closely associated with the goddess Isis, who was believed to be the mother of all life. The lunar calendar played a significant role in Egyptian agriculture and was used to determine the timing of planting and harvesting.
In Hinduism, the Moon is associated with the god Chandra, who is believed to be the ruler of the tides and the human mind. The full moon, known as Purnima, is considered a time of spiritual growth and enlightenment.
In Chinese culture, the Moon is celebrated during the Mid-Autumn Festival, which is held on the 15th day of the 8th lunar month. During this festival, families gather together to admire the Moon, eat mooncakes, and share stories and legends about the Moon.
In Greek mythology, the Moon was associated with the goddess Artemis, who was the protector of women and children. The phases of the Moon were believed to correspond to the different moods of the goddess, with the full moon representing her power and strength.
In Native American culture, the Moon was often seen as a powerful symbol of female energy and fertility. Many tribes believed that the Moon controlled the tides and the cycles of life, and they often used the lunar calendar to mark the changing seasons.
In modern times, the Moon continues to inspire and captivate people’s imaginations. The Moon landing in 1969 was a significant milestone in human history, demonstrating the power of human ingenuity and technology. Today, space agencies and private companies are once again turning their attention to the Moon, with plans to establish permanent lunar bases and explore its many mysteries.
The Role of the Moon in Shaping Earth’s Tides and Climate
The Moon is more than just a beautiful celestial body that illuminates our night sky; it plays a crucial role in shaping Earth’s tides and climate. In this blog, we will explore the active role of the Moon in shaping Earth’s natural processes and environment.
The Moon’s gravitational pull on Earth creates the ocean tides that we observe daily. As the Moon orbits around Earth, its gravity pulls on the water in the oceans, causing the water to bulge towards the Moon. This creates a high tide. At the same time, the water on the opposite side of the Earth is also pulled by the Moon’s gravity, creating a second high tide. The areas between these high tides experience low tides.
The gravitational pull of the Moon on Earth’s oceans also causes friction, which generates heat and helps to moderate the temperature of the planet. Without the Moon, Earth’s axis would be more unstable, leading to drastic climate changes and potential extinction events for many species.
In addition to its role in shaping Earth’s tides and climate, the Moon also plays a significant role in regulating the length of the day. As the Moon’s gravitational force on Earth slows down the planet’s rotation, the length of the day increases. Over time, this has had a significant impact on Earth’s climate, as changes in the length of the day can affect weather patterns and contribute to climate change.
The Moon also plays an important role in stabilizing Earth’s axial tilt, which helps to maintain a stable climate over long periods of time. Without the Moon, Earth’s axial tilt could vary significantly, leading to significant climate instability and potentially catastrophic consequences for life on our planet.
The Moon Landing: A Historic Achievement and Its Legacy
The Moon landing was a historic achievement that captivated the world and marked a new era in human exploration and technological advancement. In this blog, we will explore the active role of the Moon landing, its legacy, and the lessons we can learn from this remarkable achievement.
On July 20, 1969, the Apollo 11 mission successfully landed on the Moon, making Neil Armstrong the first human to set foot on another celestial body. This remarkable achievement marked a new era in human history, demonstrating the power of human ingenuity and technology.
The Moon landing had significant scientific and technological implications. It provided new insights into the formation and history of the Moon, as well as new opportunities for scientific research and exploration. It also spurred advances in technology, including the development of new materials, computer systems, and space travel technologies.
The legacy of the Moon landing extends far beyond science and technology. It inspired a generation of young people to pursue careers in science, engineering, and space exploration. It also demonstrated the power of international collaboration, as the United States worked with countries around the world to achieve this remarkable feat.
The Moon landing also had significant cultural and societal implications. It demonstrated the power of vision, perseverance, and teamwork, and it inspired people around the world to dream big and achieve their goals. It also sparked new conversations about the role of science and technology in society, as well as new discussions about the value of international cooperation and collaboration.
As we reflect on the legacy of the Moon landing, we can draw important lessons about the power of human potential, the value of collaboration and teamwork, and the importance of pursuing bold, visionary goals. We can also learn from the challenges and setbacks that the Apollo program faced, and the perseverance and resilience that it took to overcome them.
Lunar Phases: Understanding the Waxing and Waning of the Moon
The Moon’s phases are a beautiful and fascinating natural phenomenon that have captivated humans for thousands of years. In this blog, we will explore the active process behind the waxing and waning of the Moon, and how we can use this knowledge to understand the Moon’s phases.
The Moon’s phases are caused by its position relative to the Earth and the Sun. As the Moon orbits around the Earth, the amount of sunlight that it reflects back to Earth changes, creating the phases that we observe. The lunar cycle, which is the time it takes for the Moon to complete one orbit around the Earth, lasts approximately 29.5 days.
The four primary phases of the Moon are the new moon, first quarter, full moon, and third quarter. The new moon occurs when the Moon is between the Earth and the Sun, and the side of the Moon that faces the Earth is not illuminated. The first quarter occurs when the Moon has completed a quarter of its orbit around the Earth, and the side of the Moon that faces the Earth is half-illuminated. The full moon occurs when the Moon is on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun, and the side of the Moon that faces the Earth is fully illuminated. Finally, the third quarter occurs when the Moon has completed three-quarters of its orbit around the Earth, and the side of the Moon that faces the Earth is once again half-illuminated.
In addition to the primary phases, there are also intermediate phases, such as waxing crescent, waxing gibbous, waning gibbous, and waning crescent. These phases occur as the Moon moves between the primary phases and are characterized by varying amounts of illumination.
Understanding the Moon’s phases is not only fascinating from a scientific perspective but also has practical applications. For example, farmers have traditionally used the lunar calendar to determine the best time for planting and harvesting crops. The lunar phases can also be used to predict ocean tides and fishing patterns, as the Moon’s gravitational pull affects these natural processes.
The Dark Side of the Moon: Myths and Realities
The “Dark Side of the Moon” is a term often used to refer to the side of the Moon that is never visible from Earth. Despite its ominous name, this region of the Moon is not actually perpetually dark, and there are many myths and misconceptions surrounding this mysterious part of our celestial neighbor. In this blog, we will explore the myths and realities of the dark side of the Moon.
Contrary to popular belief, the dark side of the Moon is not always dark. The Moon rotates on its axis as it orbits around the Earth, and as a result, the far side of the Moon receives just as much sunlight as the near side. However, the term “dark side” has persisted due to the fact that this region is never visible from Earth, and therefore remains shrouded in mystery.
One of the most persistent myths about the dark side of the Moon is that it is a place of danger and mystery, home to aliens and secret government projects. However, there is no evidence to support these claims, and it is unlikely that any such activities are taking place on the Moon.
In reality, the dark side of the Moon is a region of scientific interest and exploration. In recent years, several missions have been sent to explore this uncharted territory, including China’s Chang’e 4 mission, which became the first spacecraft to land on the far side of the Moon in 2019.
Scientists are particularly interested in studying the geological differences between the near and far sides of the Moon. The far side of the Moon is characterized by a thicker crust, and the absence of large impact basins that are present on the near side. By studying these differences, scientists hope to gain new insights into the Moon’s formation and history.
Lunar Exploration: Past, Present, and Future Missions
The Moon has fascinated humans for thousands of years, and over the past century, we have made great strides in exploring this mysterious celestial body. In this blog, we will take a look at the history of lunar exploration, the current state of lunar missions, and the exciting plans for future lunar exploration.
The first successful mission to the Moon was the Soviet Union’s Luna 1, which was launched in 1959. This mission was followed by a series of missions by both the Soviet Union and the United States, including the iconic Apollo missions, which landed humans on the Moon for the first time.
In recent years, there has been renewed interest in lunar exploration, with several countries and private companies launching missions to the Moon. In 2019, China became the first country to land a spacecraft on the far side of the Moon, and in 2020, NASA launched the Artemis program, with the goal of landing the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
The current state of lunar exploration is focused on scientific research, resource exploitation, and the establishment of a permanent human presence on the Moon. Scientists are interested in studying the Moon’s geology, mineralogy, and the possibility of water ice on the Moon’s surface, which could be used as a resource for future missions.
Private companies are also getting in on the action, with several companies planning to mine the Moon for resources such as helium-3, which could be used as fuel for nuclear fusion reactors.
Looking to the future, there are many exciting plans for lunar exploration. NASA’s Artemis program aims to establish a permanent human presence on the Moon by the end of the decade, with the goal of using the Moon as a launching pad for future missions to Mars and beyond. Other countries, including China, Russia, and India, also have plans for future lunar missions.
The Moon’s Effect on Wildlife and Ecosystems
The Moon’s effect on the Earth goes beyond just its gravitational pull and its impact on tides. It also plays a role in shaping the behavior and physiology of many species of wildlife. In this blog, we will explore the ways in which the Moon affects wildlife and ecosystems.
Many species of animals, from sea turtles to birds, use the Moon’s light as a navigational tool. Some birds use the Moon as a point of reference when flying long distances, while sea turtles use the Moon to guide them to the ocean after hatching on the beach.
The Moon also affects the behavior of many nocturnal animals, including bats and moths. These animals have evolved to use the Moon’s light as a way to navigate and locate prey. In addition, some species of insects, such as fireflies, synchronize their mating behavior with the phases of the Moon.
The Moon’s impact on ecosystems is also significant. The lunar cycle affects the behavior of many marine organisms, including the timing of migrations and spawning events. The Moon’s gravitational pull also affects the movement of ocean currents, which can impact the distribution of nutrients and plankton in the water, and ultimately affect the entire food chain.
In addition, the Moon plays a role in shaping the Earth’s climate. The Moon’s gravitational pull is responsible for Earth’s axial tilt, which in turn affects the distribution of sunlight across the planet. This plays a significant role in the Earth’s climate patterns, including the timing and duration of seasons.
Moon Myths and Legends: Separating Fact from Fiction
Throughout human history, the Moon has been the subject of countless myths and legends. From stories of werewolves to tales of moon goddesses, the Moon has captured our imaginations and inspired our creativity. In this blog, we will explore some of the most popular Moon myths and legends, and separate fact from fiction.
One of the most enduring myths surrounding the Moon is the idea that it influences human behavior. Many people believe that the Moon’s phases can cause people to act erratically or experience heightened emotions. However, despite many studies, there is no scientific evidence to support this claim.
Another popular Moon myth is the story of the “man in the Moon.” This myth suggests that the dark patches on the Moon’s surface form the image of a man’s face. However, this is simply an example of pareidolia, the human tendency to see familiar shapes and patterns in random objects.
Many cultures have also created myths and legends surrounding lunar eclipses. In ancient times, people believed that lunar eclipses were a sign of impending doom, while others saw them as a time of great change or transformation. In reality, lunar eclipses occur when the Earth passes between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon’s surface.
The Moon has also been the subject of many religious and spiritual beliefs. In many cultures, the Moon is seen as a powerful symbol of femininity and fertility, associated with goddesses such as Artemis and Selene. In other traditions, the Moon is associated with death and rebirth, and is seen as a gateway to the afterlife.
Lunar Observations: Tips and Tools for Stargazers and Astronomers
The Moon is a fascinating object to observe in the night sky, whether you are a seasoned astronomer or a casual stargazer. In this blog, we will provide some tips and tools for observing the Moon and making the most of your lunar observations.
First and foremost, it is important to find a location with minimal light pollution. The Moon is bright, but its subtle features can be obscured by bright lights. If possible, try to observe the Moon from a dark location, away from streetlights and other sources of light pollution.
When observing the Moon, it is helpful to use a telescope or binoculars. These tools can bring the Moon’s craters, mountains, and other features into sharp focus. Look for areas of light and shadow, as well as the “terminator,” the line between the illuminated and dark portions of the Moon.
Another useful tool for lunar observation is a lunar filter. These filters can help reduce the Moon’s brightness, making it easier to see details on the surface. Some filters also enhance the contrast of the lunar features, making them more visible.
It is also important to observe the Moon at the right time. The best time to observe the Moon is during its waxing and waning phases, when the terminator is visible and the shadows cast by craters and mountains are more pronounced. The full Moon can be an impressive sight, but its brightness can make it difficult to see details on the surface.
Finally, it is important to be patient when observing the Moon. The best views often come with careful observation and a little bit of patience. Take your time and enjoy the beauty and complexity of our nearest celestial neighbor.