Topic: Introduction to Jupiter
- Overview of Jupiter’s size, distance from the Sun, and other basic facts
- History of observations and exploration of Jupiter
- Importance of studying Jupiter for our understanding of the solar system
Topic: Physical Characteristics of Jupiter
- Composition and structure of Jupiter’s atmosphere
- Great Red Spot and other atmospheric features
- Interior structure and magnetic field of Jupiter
Topic: Moons of Jupiter
- Overview of Jupiter’s four largest moons (Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto)
- Unique features of each moon, such as volcanic activity on Io and possible subsurface oceans on Europa
- Importance of studying Jupiter’s moons for understanding the potential for life elsewhere in the solar system
Topic: Exploration of Jupiter
- Overview of past and current missions to Jupiter, such as the Voyager, Galileo, and Juno missions
- Key discoveries made by these missions, such as evidence of a subsurface ocean on Europa and new information about Jupiter’s magnetic field
- Future plans for exploring Jupiter, such as the planned Europa Clipper mission
Topic: Jupiter in Popular Culture
- Depictions of Jupiter in mythology and literature
- Jupiter in science fiction, such as the movie “2001: A Space Odyssey” and the novel “The Sirens of Titan”
- How our understanding of Jupiter has influenced our perception of the universe
Introduction to Jupiter
Physical Characteristics of Jupiter
Jupiter is the largest planet in our solar system, and its physical characteristics are as fascinating as they are unique. In this blog post, we’ll explore some of the key features that make Jupiter so intriguing, including its atmosphere, magnetic field, and interior structure.
Atmosphere of Jupiter
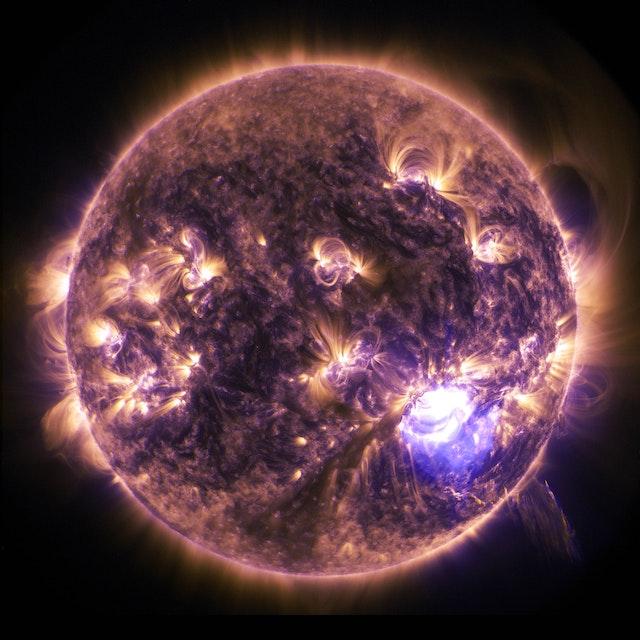
Jupiter’s atmosphere is incredibly thick and composed primarily of hydrogen and helium gas. The clouds in Jupiter’s atmosphere are made up of different colors and patterns, giving the planet a distinctive appearance. The Great Red Spot, a massive storm that has been raging on Jupiter for centuries, is one of the most famous features of the planet’s atmosphere.
Scientists have also observed other large storms on Jupiter, including the Oval BA, a storm that was first observed in 2000 and is still going strong today. These storms can provide valuable insights into the planet’s atmospheric dynamics and can help us understand more about the formation and evolution of gas giant planets like Jupiter.
Magnetic Field of Jupiter
Jupiter has a strong magnetic field that is 20,000 times stronger than Earth’s. This magnetic field plays a crucial role in shaping Jupiter’s environment and protecting the planet from the solar wind. The magnetic field also creates spectacular auroras in Jupiter’s polar regions, much like the auroras that can be seen on Earth.
One of the most interesting aspects of Jupiter’s magnetic field is its interaction with its moons. Io, one of Jupiter’s largest moons, is surrounded by a plasma torus that is created by the interaction between Io’s atmosphere and Jupiter’s magnetic field. This torus creates a beautiful glow around Io that can be seen from Earth.
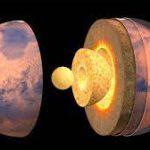
Interior Structure of Jupiter
While the outer layers of Jupiter are composed of gas, the planet’s interior is thought to be quite different. Scientists believe that Jupiter has a rocky, metallic core that is surrounded by layers of liquid metallic hydrogen. This hydrogen is compressed to such a degree that it behaves like a metal, conducting electricity and creating Jupiter’s strong magnetic field.
Jupiter’s interior structure is still not well understood, but recent studies have provided some new insights. In 2018, for example, scientists used data from the Juno mission to study Jupiter’s gravity field and found evidence of a “fuzzy” core that is not as well-defined as previously thought.
Moons of Jupiter
Names and Sizes of Jupiter’s Moons
Jupiter’s moons are named after figures from Greek and Roman mythology, as well as after lovers and descendants of the god Jupiter. The four largest moons of Jupiter, known as the Galilean moons, are Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto. These moons were first observed by the astronomer Galileo Galilei in 1610 and are still some of the most fascinating objects in our solar system.
Io is the closest of the Galilean moons to Jupiter and is known for its active volcanoes and its colorful surface. Europa, the second-closest moon, has a smooth and icy surface that scientists believe covers a subsurface ocean. Ganymede is the largest moon in the solar system and is larger than the planet Mercury. Callisto, the outermost of the Galilean moons, is heavily cratered and is believed to have a subsurface ocean as well.
In addition to the Galilean moons, Jupiter has many smaller moons that are less well-known. These moons have a wide range of sizes, with some being only a few kilometers in diameter and others being several hundred kilometers across.
Unique Features of Jupiter’s Moons
Each of Jupiter’s moons has its own unique features and characteristics. For example, Io is the most volcanically active object in the solar system, with hundreds of active volcanoes spewing lava and sulfur dioxide. Europa’s smooth and icy surface is thought to cover a subsurface ocean that could potentially harbor life. Ganymede is the only moon in the solar system known to have its own magnetic field, while Callisto has one of the oldest and most heavily cratered surfaces of any object in the solar system.
Jupiter’s moons also interact with one another in interesting ways. For example, the strong gravitational forces between the Galilean moons create a complex dance in which they orbit around Jupiter in a synchronized pattern. This dance is known as a Laplace resonance and helps to stabilize the orbits of the moons.
Exploration of Jupiter: Past, Present, and Future
Overview of Past and Current Missions
The exploration of Jupiter began in 1973 with the launch of NASA’s Pioneer 10 spacecraft. This mission provided the first close-up images of Jupiter and its moons, as well as valuable data on the planet’s magnetic field and radiation environment. In 1979, the Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 spacecraft provided even more detailed information about Jupiter, its moons, and its rings. Voyager 2 also provided the first-ever views of Jupiter’s polar regions.
In 1989, NASA’s Galileo spacecraft was launched on a mission to study Jupiter and its moons in even greater detail. Galileo spent eight years in orbit around Jupiter, during which time it discovered several new moons and made many important scientific discoveries. These included evidence of a subsurface ocean on the moon Europa, evidence of volcanic activity on the moon Io, and a better understanding of Jupiter’s powerful magnetic field.
Most recently, in 2011, NASA’s Juno spacecraft was launched on a mission to study Jupiter’s atmosphere, interior structure, and magnetic field. Juno arrived at Jupiter in 2016 and has been orbiting the planet ever since, providing stunning images and valuable scientific data. Juno has already made several important discoveries, including the detection of a previously unknown radiation belt around Jupiter’s equator.
Key Discoveries Made by Past Missions
Over the years, the missions to Jupiter have made many important discoveries. Some of the most significant ones are:
- Evidence of a subsurface ocean on Europa: The Galileo mission provided strong evidence that Europa, one of Jupiter’s moons, has a subsurface ocean of liquid water. This has led to speculation that Europa could harbor life.
- Volcanic activity on Io: The Voyager and Galileo missions revealed that Io, another of Jupiter’s moons, is one of the most volcanically active bodies in the solar system.
- Jupiter’s powerful magnetic field: The Voyager and Galileo missions discovered that Jupiter has an incredibly powerful magnetic field that is 20,000 times stronger than Earth’s. This magnetic field traps high-energy particles and creates intense radiation belts around the planet.
Future Plans for Exploring Jupiter
There are several planned missions to Jupiter in the coming years, including:
- Europa Clipper: This NASA mission is set to launch in the 2020s and will study Europa in detail, including its potential habitability.
- JUICE: This European Space Agency mission is set to launch in 2022 and will study Jupiter and its moons, with a focus on the potentially habitable moons Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto.
- NASA’s New Frontiers 4: This mission is still in the planning stages but is expected to focus on exploring Uranus and/or Neptune. However, Jupiter and its moons could also be studied as part of the mission.
Jupiter in Popular Culture: From Mythology to Science Fiction
Depictions of Jupiter in Mythology and Literature
Jupiter has been a central figure in Roman mythology, where he was known as the king of the gods. He was often depicted with a thunderbolt in his hand, and his symbol was the eagle. In Greek mythology, Jupiter was known as Zeus and was also considered the king of the gods. His thunderbolts were said to be capable of causing earthquakes and other natural disasters.
Jupiter’s influence can also be seen in literature. In Dante’s “Divine Comedy,” Jupiter is depicted as the embodiment of justice and is responsible for maintaining order in the universe. In Shakespeare’s “Cymbeline,” Jupiter is a benevolent deity who intervenes to restore order and happiness to the play’s characters.
Jupiter in Science Fiction
Jupiter’s status as the largest planet in our solar system has made it a popular subject in science fiction. One of the most famous examples is the movie “2001: A Space Odyssey,” where Jupiter plays a central role in the story’s climax. In the movie, a spacecraft is sent to Jupiter to investigate a mysterious monolith that is believed to be of extraterrestrial origin.
Another notable example of Jupiter in science fiction is Kurt Vonnegut’s novel “The Sirens of Titan.” In the book, Jupiter is depicted as a kind of cosmic joke, with a society of aliens manipulating events on Earth in order to eventually send a spaceship to Jupiter, where it crashes and the survivors are forced to live out the rest of their lives in a kind of purgatory.
Jupiter’s Influence on Our Perception of the Universe
Our understanding of Jupiter has had a significant influence on our perception of the universe. Jupiter’s size and composition have helped scientists better understand how planets form and evolve. Its powerful magnetic field has also been the subject of study, providing insight into how magnetic fields work in other parts of the universe.
Jupiter’s role in science fiction has also contributed to our understanding of the universe. From “2001: A Space Odyssey” to “The Sirens of Titan,” Jupiter has been used to explore themes of extraterrestrial life, the mysteries of the universe, and the limitations of human understanding.